The health value of resveratrol and its correct use
 Hongji Medical
Hongji Medical- Jan 30
- 6 min read
1. What is resveratrol?
Resveratrol is a natural polyphenol compound that was first isolated from the root of white hellebore by Japanese scholar Takaoka in 1939. Resveratrol belongs to the stilbenoid class of compounds and is classified as a polyphenol compound because of its structure containing two phenol rings.
The main function of resveratrol in plants is to help them resist external environmental stimuli, such as excessive ultraviolet light, bacterial or fungal infections, etc. Currently, more than 70 species of plants have been found to be able to synthesize resveratrol.
There are two isomeric forms of resveratrol: cis and trans. Trans resveratrol is more common in nature, and its structure is more stable than cis, and it is also the main form in which resveratrol exerts its physiological activity. In addition, resveratrol monomers can be polymerized into polymers, with the degree of polymerization ranging from two to eight. At least 92 types of resveratrol and its polymers have been discovered so far.

Origin of Resveratrol
Resveratrol was first discovered in the plant white hellebore, which is used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat a variety of diseases. With the deepening of scientific research, the health value of resveratrol has gradually been revealed, especially its potential in anti-oxidation, anti-inflammatory and anti-aging.
Chemical structure of resveratrol
The chemical structure of resveratrol is composed of two benzene rings and one vinyl group, which gives it a strong antioxidant capacity. Due to its stable structure, trans-resveratrol is more easily absorbed and utilized by the human body, so it has received more attention in research and application.
2. Absorption and Utilization of Resveratrol
Resveratrol is poorly soluble in water, which means it needs the assistance of other proteins in the transport of nutrients. The half-life of resveratrol is very short, and about 77% of resveratrol and its metabolites will be excreted from the body within 4 hours after ingestion, which indicates that the amount of resveratrol that can actually be utilized is not much, so its bioavailability is considered to be low.
Factors Affecting Absorption
The absorption of resveratrol is affected by many factors, including the fat content of the diet, individual metabolic differences, and the intake of other nutrients. A high-fat diet reduces the absorption rate of resveratrol, while certain nutrients such as ribose and piperine can increase its bioavailability.
Methods to improve bioavailability
To increase the bioavailability of resveratrol, the following methods may be considered:
Choose the morning time for supplementation , as the gastrointestinal tract has a stronger absorption capacity at this time.
Pair it with foods rich in ribose and piperine , such as black pepper and certain fruits.
Avoid taking resveratrol immediately after a high-fat meal.
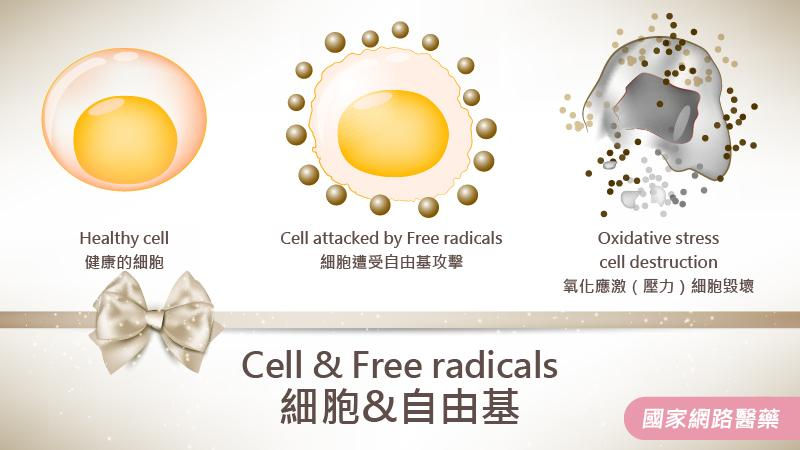
3. What are the effects of resveratrol?
Helps improve metabolism
Resveratrol helps improve metabolism in the body, helps the body function healthily and efficiently, and maintains vitality. It can activate a gene called SIRT1, which is related to cell metabolism and lifespan.
Maintain physiological functions
As a polyphenol compound, resveratrol helps maintain physiological functions, supports the body's overall health, and makes people feel more energetic. It has strong antioxidant properties that can neutralize free radicals and reduce cell damage.
Beauty and youthful vitality
Resveratrol can help coordinate the inner balance, maintain beauty, maintain youthful vitality, and make people who love beauty glow with confidence. It can promote the synthesis of collagen and improve skin elasticity and firmness.
Maintain strength and endurance
Resveratrol helps boost strength and endurance, allowing you to perform better in daily activities and sports. It can improve muscle function and reduce fatigue after exercise.

4. Who should take Resveratrol?
People who need beauty care
People with irregular work and rest schedules and high stress in life
Middle-aged and older people maintain youthful vitality
Want to help metabolism and enhance physical strength
Benefits for specific groups
Beauty and skin care seekers : The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of resveratrol help improve skin texture and reduce wrinkles.
People with irregular work and rest schedules and high stress in life : Resveratrol can help reduce the negative effects of stress on the body and maintain physiological balance.
Middle-aged and older people : Resveratrol helps slow down the aging process and maintain youthful vitality.
Metabolism and physical strength enhancer : Resveratrol can enhance metabolism, enhance physical strength and endurance.
5. How much resveratrol should be taken?
Resveratrol is relatively safe, but the dosages studied in different countries vary greatly, ranging from a low dose of 5 mg/day to a high dose of 5 g/day.
Effects of different doses
Low dose (5-50 mg/day) : suitable for daily care and maintaining basic health.
Moderate doses (50-400 mg/day) : Suitable for people with specific health needs, such as improving skin conditions or increasing physical strength.
High doses (>400 mg/day) : Need to be used under the guidance of a medical professional and are suitable for people with serious health problems or who need quick results.
6. What foods contain resveratrol?
Resveratrol was first isolated from the herb Resveratrol, and was later found in other herbs such as Japanese knotweed. Resveratrol is also found in common foods, especially fruits, nuts and their processed products, including: grapes (red), red wine, tomato skin, apples, pomegranates, blueberries, mulberries, peanuts and chocolate.

Resveratrol Content in Food
Grapes (red) : Contains approximately 0.2-5.8 mg of resveratrol per 100 grams.
Red wine : contains about 1-14 mg of resveratrol per liter.
Peanuts : Each 100 grams contains about 0.01-1.8 mg of resveratrol.
Chocolate : Contains about 0.1-1.5 mg of resveratrol per 100 grams.
7. How to take resveratrol? Is it better to take it before or after a meal?
Taking resveratrol in the morning can help improve its bioavailability. The absorption rate of resveratrol is affected by individual differences. Studies have found that a high-fat diet will reduce its bioavailability; on the contrary, taking it with ribose and piperine can improve its bioavailability.
Best time to replenish
Morning : The gastrointestinal absorption capacity is stronger, which is suitable for supplementing resveratrol.
Before meals : avoid interference from high-fat diets to improve absorption rate.
Combined with ribose and piperine : can further improve the bioavailability of resveratrol.
8. Contraindications and side effects of resveratrol
Although resveratrol is fairly safe to supplement, high doses (>1 g/day) may cause digestive discomfort. Resveratrol can also interfere with drug metabolism, so if you are taking medication, you should consult a healthcare professional before taking a supplement.
Common Side Effects
Digestive discomfort : High doses of resveratrol may cause symptoms such as indigestion, bloating, and diarrhea.
Drug Interactions : Resveratrol may affect the metabolism of certain drugs, especially those that are metabolized by the liver, such as anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory drugs, and some blood pressure medications.
How to avoid side effects
Moderate intake : Follow the recommended daily intake and avoid overdose.
Talk to your doctor : Before starting to supplement with resveratrol, especially if you are taking other medications, you should talk to your healthcare professional.
Monitor your body's reactions : Pay attention to your body's reactions. If you feel uncomfortable, stop using the product immediately and seek medical advice.
9. Who should not take resveratrol?
People with blood clotting problems : Resveratrol may affect blood clotting and is not suitable for people with blood clotting problems.
Those who are planning to undergo surgery : Stop taking resveratrol before surgery to avoid affecting blood coagulation during surgery.
Not suitable for use with NSAIDs : Resveratrol may increase the side effects of NSAIDs.
It is not recommended for pregnant and breastfeeding women to take additional resveratrol supplements : Due to the lack of sufficient safety data, pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid taking additional resveratrol supplements.
Precautions for special populations
Pregnant and breastfeeding women : Since resveratrol may be passed to the baby through the placenta or breast milk and affect the baby's health, it is not recommended for use.
Surgical patients : Resveratrol should be discontinued at least two weeks before surgery to avoid affecting blood clotting during surgery.
Patients with chronic diseases : If you have chronic diseases, especially liver disease, kidney disease or blood disease, you should use resveratrol under the guidance of a doctor.
In short, resveratrol and collagen are both important ingredients in modern beauty care, and they each have unique health values and effects. Understanding the sources, effects and usage of these ingredients can help us better choose health foods that are suitable for us to achieve the goal of maintaining beauty and youthful vitality.





